|
In the case of orientation
polarization we have a material with built-in dipoles that are
independent of each other, i.e. they can rotate freely - in sharp contrast
to ionic polarization. |
|
 |
The prime example is liquid water, where every
water molecule is a little dipole that can have any orientation with respect to the other molecules. Moreover, the orientation
changes all the time because the molecules moves!
Orientation polarization for dielectric dipoles thus is pretty much limited to liquids - but we will encounter it in a major
way again for magnetic dipoles. |
|
 |
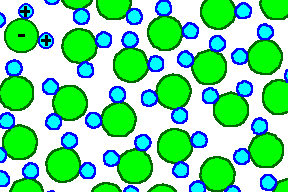
A two-dimensional "piece of water" may - very graphically - look somewhat
like the picture below that captures one particular moment in time. It is like a snapshot
with a very, very short exposure time. A few nanoseconds later the same piece of water may look totally different in detail,
but pretty much the same in general. |
|
 |
In a three-dimensional piece of water the blue and red circles would not have
to be in the same plane; but that is easy to imagine and difficut to draw. |
| |
|
|
 |
Shown is a bunch of water molecules that form natural dipoles because the negatively
charged oxygen atom and the two positively charged H - atoms have different centers of charge. Each molecule carries
a dipole moment which can be drawn as a vector of constant length. If we only draw a vector denoting the dipole moment,
we get - in two dimensions - a picture like this: |
|
|
|
|
 |
Again, remember that both pictures are "snap shots"
that only appear unblurred for very small exposure times, say picoseconds, because the dipoles wiggle, rotate, and move
around rather fast, and that in three dimensions the vectors would also point out of
the drawing plane. |
 |
The total dipole moment is the vector sum of the individual dipole moments. |
| |
| |
|
 |
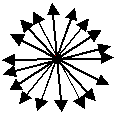
For dipoles oriented at random, at any
given moment this looks like the picture below if we draw all vectors from a common origin: The sum of all dipole moments
will be zero, if the dipoles are randomly oriented. |
 |
We can see this most easily if we have all dipoles start at the same origin. The picture,
of course, is two-dimensional and crossly simplified. There would be a lot more (like 10 20) dipoles for
any appreciable amount of water - you really will average them to zero pretty well. |
 |
In reality, the orientation into the field direction will be counteracted
by random collisions with other dipoles, and this process is energized by the thermal
energy "kT" contained in the water. |
|
 |
Again, the dipoles are not sitting still, but moving around and rotating all
the time - because they contain thermal energy and thus also some entropy.
|
|
 |
Whenever two molecules collide, their new orientation is random
- all memory of an orientation that they might have had in the electrical field is lost. This
is analogous to what happens to electrons carrying an electrical current in an electrical field. |
|
 |
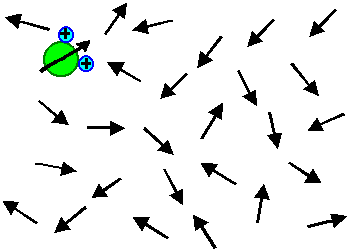
The electrical field only induces a little bit of average
orientation in field direction - most of the time an individual dipole points in all kinds of directions. This is the simple
truth even so some (undergraduate) text books show pictures to the contrary.
The "real" picture (in the sense of a snapshot with a very short exposure time) looks like this: |
| |
 |
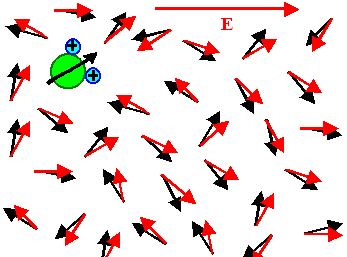 |
| Without field | With field |
|
|
 |
The orientation of all dipoles is just a little bit shifted so that an average orientation
in field direction results. In the picture, the effect is even exaggerated! |
 |
In fact, the state of being liquid by necessity
implies quite a bit of entropy, and entropy means disorder.
|
|
 |
Perfectly aligned dipoles would be in perfect order without
any entropy - this is only possible at extremely low temperatures (and even there quantum theory would not allow it) where
we will not have liquids any more, or more generally, dipoles that are able to rotate freely. |
|
 |
In other words, we must look for the minimum of the free enthalpy
G and not for the minimum of the internal energy
U. At finite temperatures the minimum of the free enthalpy requires some entropy
S, i.e. randomness in the
dipole orientation, so we should not expect perfect orientation. |
 |
If you are not familiar with the basics of thermodynamics, you
have a problem at this point. If you do know your thermodynamics, but are a bit insecure, turn to the basic module "Thermodynamics" (in the "Defects"
Hyperscript) to refresh your memory. |
 |
We obviously need to calculate the free enthalpy G=U – TS to
see what kind of average orientation will result in a given field. Note that we use U, the common symbol for
the (internal) energy instead of H, the common symbol for the enthalpy, because U and H
are practically identical for solids and liquids anyway. |
|
 |
Moreover, a mix up with the magnetic field strength usually designated by
H, too, would be unavoidable otherwise. (The possible mix-up between internal energy U and voltage
U is not quite so dangerous in this context). |
 |
The internal energy od a dipole is clearly a function of its orientation with
respect to the field. It must be minimal, when the dipole is aligned with the field and thedipole
moment has the same direction as the electrical field, and maximal if the direction is reversed. |
|
 |
This is the easy part: The energy U(d)
of a dipole with dipole moment m in a field E as a function of the angle
d ("delta") between the dipole moment direction and the field direction. |
| |
|
|
|
|  |
From basic electrostatics we have have |
| |
|
| U(d) = |
– m · E = |
– |m| · |E| · cos d
|
|
|
 |
The minimum energy
U thus would occur for d=0o, i.e. for perfect alignment in proper
field direction (note the minus sign!); the maximum energy for d=180o,
i.e. for alignment the wrong way around. |
 |
That was for two dimensions - now we must look at this in three
dimensions. |
| |
|
|
 |
In 3D we see that all dipoles with the same angle d
between their axis and the field still have the same energy - and this means now all dipoles on a cone
with opening angle 2d around the field axis if we consider possible orientations out of the plane of drawing.
|
|
 |
In order to obtain the total internal energy
Utotal of a bunch of dipoles having all
kinds of angles d with the field axis, we will have to sum up all cones.
|
|
 |
This means we take the number of dipoles N(d)
having a particular orientation d times the energy belonging to that d,
and integrate the resulting function over d from 0o to 180o.
This is something that we could do - if we would know N(d). |
 |
However, just calcuating Utotal will not be of much use.
We also must consider the entropy term – TS, because we do not want
to calculate the total internal energy
Utotal, but the total free enthalpy
G=Utotal – TS. |
|
 |
We need to consider that term as a function of all possible angle distributions
and then see for which distribution we can minimize G. |
 |
But what is the entropy
S(N(d)) of an ensemble of dipoles containing N(d)
members at the angle d as a function of the many possible distribution N(d)? Not an easy question to answer from just looking at the dipoles. |
|
|
Fortunately, we do not have to calculate S explicitly! |
|
 |
We know a formula for the distribution of
(classical) particles on available energy levels that automatically gives the minimum
of the free enthalpy! |
|
 |
We have a classical system where a number
of independent particles (the dipoles) can occupy a number of energy levels (between
Umin and Umax) as defined by d=0o
or d=180o, respectively. |
|
 |
Basic thermodynamics asserts that in equilibrium,
the distribution of the particles on the available energy levels is given by the proper distribution
function which is defined in such a way that it always gives the minimum
of the free enthalpy. |
|
 |
Since we deal with classical particles in this approach, we have to use the Boltzmann
distribution. We obtain for N(U)= number of dipoles with the energy
U |
| |
|
|
 |
With a constant A that has yet to be determined. |
 |
This Boltzmann distribution equation gives us the number of dipoles with a certain
angle relative to the field direction, i.e. the number of dipoles that have their tips on a circle with an opening angle
2d relative to the field directions as shown below. |
| |
|
|
 |
We are, however, only interested in the component of
the dipole moment parallel to the field. For this we look at the solid angle increment dW defined on the unit sphere as the segment between d and d + dd. |
|
| |
| |
|
 |
The number of dipoles lying in the cone angle increment defined
by d and d+ Dd is the same
as the number of dipoles with tips ending on the surface of the unit sphere in the incremental angle dW.
It is given by
N(U(d)) · dW.
|
 |
Note that dW is a measure of an incremental area;
a kind of ribbon once around the unit sphere. |
 |
The sum of the components mF of the dipole moments
in field direction is then
. |
|
| mF = (N · dW) · (m
· cos d) |
|
|
| |
|
 |
If you are not familiar with spherical coordinates, this (and what we will do
with it), looks a bit like magic. Since we do not want to learn Math in this lecture, the essentials to spherical
coordinates are explained in detail in a basic module. |
 |
The average dipole moment, which is what we
want to calculate, will now be obtained by summing up the contributions from all the dWs |
| |
|
<mF> = |
p
ó
õ
0 |
N(U(d)) · m · cosd
· dW |
|
|
|
|
 |
And the integrals have to be taken from the "top" of the sphere to the
"bottom" , i.e. from 0 to p. |
 |
dW and d
are of course closely related, we simply have |
| |
|
 |
Putting everything together, we obtain a pretty horrifying integral for mF that runs from 0 to p |
| |
|
<mF> = |
| m · |
p
ó
õ
0 |
sind · cosd · exp |
m · E · cosd
kT | · dd |
p
ó
õ
0 | sind · exp |
m · E · cosd
kT | · dd |
|
|
|
 |
One advantage is that we got rid of the undetermined constant A.
The integral, being a determined integral, is now simply a number depending on the parameters
of the system, i.e. the temperature T, the dipole moment m and the field
strength E. |
|
 |
The problem has been reduced to a mathematical exercise
in solving integrals. |
 |
Since we are not interested at doing math, we just show the general direction
toward a solution: |
|
 |
Use the substitutions |
|
|
|
|
 |
The integral reduces to
|
| |
|
<mF> = |
| m · |
–1
ó
õ
+1 |
x · exp (b · x) · dx |
–1
ó
õ
+1 | exp (b · x) · dx |
|
|
|
 |
The final result after quite a bit of fiddling around is
|
| |
|
|
 |
With L(b)=Langevin
function, named after Paul Langevin,
and defined as
. |
| |
|
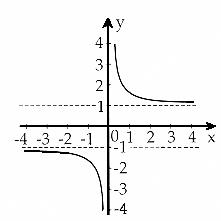
y=coth x |
|
|
 |
The "coth" is the hyperbolic cotangent, defined as coth x=(ex + e–x)/(ex
– e–x)=1/tanh x. |
|
 |
L(b) is a tricky function, because the coth
x part looks pretty much like a hyperbola, from which the real hyperbola 1/x is subtracted. What's
left is almost nothing - L(x) values are between 0 and 1 |
 |
The polarization (always on average, too) is accordingly
. |
| |
|
 |
This is a definite result, but it does not help much. We need to discuss the mathematical
construct "Langevin function
L(b)" to get some idea of what we obtained. We look at the graph in general units
and in units of the dipole moment and electrical field (in red). |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Since b is proportional to the field strength
E, we see that the dipole moment and the polarization increases monotonically with E, eventually
saturating and giving <µF>=µ which is what we must expect.
|
| |
 |
The question is, what range of b
values is accessible for real materials. i.e. how close to the saturation limit can we get? |
| | |
| |
 |
For that we look at some simple approximations. |
|
 |
If we develop L(b) into a series (consult a math textbook), we get
|
| |
|
|
|
| L(b) = |
b
3 |
– |
b3
45 |
+ |
2 b5
945
|
– ..... |
|
|
| |
|
|
 |
For large values of b we have
L(b) » 1, while for small values of b (b < 1), the Langevin function can be approximated
by . |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
 |
The slope thus is 1/3 for b
® 0. |
|
 |
For "normal" circumstances, we always have b << 1 (see below), and we obtain as final result for the induced
dipole moment the Langevin - Debye equation |
| |
| <mF> | = |
m2 · E
3kT |
| | | |
| <P> | = |
N · m2 ·E
3kT |
|
|
| |
|
|
 |
These equations will be rather good approximation for small values of m and E and/or large values of T. For very large fields and very small temperatures
the average dipole moment would be equal to the built in dipole moment, i.e. all dipoles would be strictly parallel to the
field. This is, however, not observed in "normal" ranges of fields and temperatures. |
 |
Lets see that in an example. We take |
|
 |
E=108 V/cm which is about the highest field strength imaginable before we have electrical breakdown,
m=10–2 9 Asm, which is a large dipole moment for a strongly polarized
molecule, e.g. for HCl, and
T=300 K. |
|
 |
This gives us
b=0,24 - the approximation is still valid. You may want to consult exercise
3.2-1 again (or for the first time) at this point and look at the same question from a different angle. |
 |
At T=30 K, however, we have b=2,4
and now we must think twice: |
|
 |
1. The approximation would no longer be good. But
|
|
 |
2. We no longer would have liquid
HCl (or H2O, or liquid whatever with a dipole moment), but solid HCl (or whatever) , and
we now look at ionic polarization and no longer at orientation polarization! |
 |
You may now feel that this was a rather useless exercise - after all, who is interested
in the DK of liquids? But consider: This treatment is not restricted to electric
dipoles. It is valid for all kinds of dipoles that can rotate freely, in particular for the magnetic
dipoles in paramagnetic materials responding to a magnetic field. |
|
 |
Again, you may react with stating "Who is interested in paramagnets? Not
an electrical engineer!" Right - but the path to ferromagnets, which definitely
are of interest, starts exactly where orientation polarization ends; you cannot avoid it. |
 |
It is important to be aware of the basic condition that we made
at the beginning: there is no interaction between the dipoles! This will not be true in general.
|
|
 |
Two water molecules coming in close contact will of course "feel" each
other and they may have preferred orientations of their dipole moments relative to each other. In this case we will have
to modify the calculations; the above equations may no longer be a good approximation. |
|
 |
On the other hand, if there is a strong interaction,
we automatically have some bonding and obtain a solid - ice in the case of water. The dipoles most likely cannot orientate
themselves freely; we have a different situation (usually ionic polarization). There are, however, some solids where dipoles
exist that can rotate to some extent - we will get very special effects, e.g. "ferroelectricity". |
| |
|
© H. Föll (Electronic Materials - Script)