|
In this subchapter we will give an outline of how to progress
from the simple version of Ohms
"Law", which is a kind of "electrical" definition for a black box, to
a formulation of the same law from a materials point of view employing (almost) first
principles. | |
|
|
 |
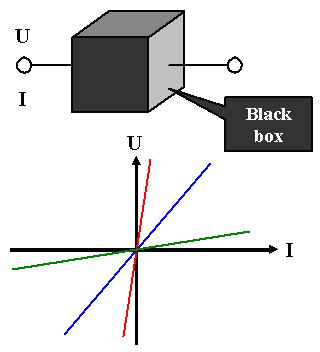
In other words: The electrical engineering point of view
is: If a "black box" exhibits a linear relation between the (dc) current I
flowing through it and the voltage U applied to it, it is an ohmic resistor. |
|
|
 |
That is illustrated in the picture: As long as the voltage-current characteristic you measure between two
terminals of the black box is linear, the black box is called an (ohmic) resistor). |
|
|
 |
Neither the slope of the I-U-characteristics matters, nor the material content of the box. |
|
 |
TheMaterials Science point of view is quite different.
Taken to the extreme, it is: | |
|
 |
Tell me what kind of material is in the black box, and I tell you:
- If it really is an ohmic resistor, i.e. if
the current relates linearly to the voltage for reasonable voltages and both
polarities.
- What its (specific) resistance will be, including its temperature dependence.
- And everything else of interest.
| |
 |
In what follows we will see, what we have to do for this approach. We will proceed in 3
steps | |
|
 |
In the first two steps, contained in this sub-chapter we simply reformulate Ohms law in physical
quantities that are related to material properties. In other words, we look at the properties of the moving charges that
produce an electrical current. But we only define the necessary quantities; we do not
calculate their numerical values. |
|
 |
In the third step - which is the content of many chapters - we will find ways to actually calculate the important quantities, in particular for semiconductors. As it turns out, this is
not just difficult with classical physics, but simply impossible. We will need a good dose of quantum mechanics and statistical
thermodynamics to get results. |
| | |
| |
 |
The "global" field strength is |
|
|
|
|
 |
With l = length of the body. If we want the local
field strength E(x,y,z) as a vector, we have, in principle, to solve the Poisson equation |
| |
| Ñ · E(x,y,z) = |
r(x,y,z)
ee0 |
|
|
|
 |
With r(x,y,z) =
charge density.
For a homogeneous materisl with constant cross section, however, E is parallel to f and
constant everywhere, again which is clear without calculation. |
 |
So. to make things easy, for a homogenous material of length l with constant
cross-sectional area F, the field strength E and the current density j
do not depend on position - they have the same numerical value everywhere. |
|
 |
For this case we can now write down Ohms law with the new quantities and obtain |
| |
| j · F = I = |
1
R | · U |
= | 1
R |
· E · l |
|
|
 |
The fraction l/ F · R
obviously
(think about it!) has the same numerical value for any
homogeneous cube (or homogeneous whatever) of a given material; it is, of course, the specific
conductivity s |
| |
|
|
 |
and r is the specific
resistivity. In words: A 1 cm3 cube of homogeneous material
having the specific resistivity r has the resistance R = (r
· l)/F |
|
 |
Of course, we will never mix up the specific resistivity
r with the charge density
r or general densities
r, because we know from the context what is meant! |
|  |
The specific resistivity obtained in this way is necessarily
identical to what you would define as specific resistivity by looking at some rectangular body with cross-sectional area
F and length l. |
|
 |
The specific conductivity has the dimension [s] = W–1cm–1, the dimension of the
specific resistivity is [r] = Wcm.
The latter is more prominent and you should at least have a feeling for representative numbers by remembering |
| |
| r (metal) |
» |
2 µWcm | | |
| |
| r (semicoductor) |
» |
1 Wcm | | |
| |
| r (insulator) |
» |
1 GWcm |
|
|
 |
Restricting ourselves to isotropic and homogenoeus materials, restricts s and r to being scalars
with the same numerical value everywhere, and Ohms law now can be formulated for any
material with weird shapes and being quite inhomogeneous; we "simply" have |
| |
|
 |
Ohms law in this vector form is now valid at any
point of a body, since we do not have to make assumptions about the shape of the body. |
|  |
Take an arbitrarily shaped body with current flowing through it, cut out a little cube (with
your "mathematical" knife) at the coordinates (x,y,z) without changing the flow of current, and
you must find that the local current density and the local field strength obey the equation given above
locally. |
| |
|
|
 |
Of course, obtaining the external current I flowing for the external voltage
U now needs summing up the contributions of all the little cubes, i.e. integration over the whole volume,
which may not be an easy thing to do. |
 |
Still, we have now a much more powerful version of Ohms law! But we should now harbor a certain
suspicion: |
|
 |
There is no good reason why j must always be parallel
to E. This means that for the most general case s is not a scalar quantity, but a tensor; s = sij.
(There is no good way to write tensors in html; we use the ij index to indicate
tensor properties. |
|
 |
Ohms law then writes |
| |
jx = sxx · Ex
+ sxy · Ey + sxz
· Ez
jy = syx · Ex + syy
· Ey + syz · Ez
jz = szx · Ex + szy
· Ey + szz · Ez |
|
|
 |
For anisotropic inhomogeneous materials you have to take the tensor, and its components will
all depend on the coordinates - that is the most general version of Ohms law. |
|
 |
Note that this is not so general as to be meaningless:
We still have the basic property of Ohms law: The local current density is directly proprotional to the local field strength
(and not, for example, to exp– [const. · E] ). |
 |
Our goal now is to find a relation that allows to calculate sij
for a given material (or material composite); i.e. we are looking for |
|
 |
sij = sij(material,
temperature, pressure, defects... ) |
| |
|
|
2. Step: Describe sij
in Terms of the Carrier Properties |
| |
|
 |
Electrical current needs mobile charged "things"
or carriers that are mobile. Note that we do not
automatically assume that the charged "things" are always electrons. Anything charged and mobile will do. |
 |
What we want to do now is to express sij in terms
of the properties of the carriers present in the material under investigation. |
|
 |
To do this, we will express an electrical current as a "mechanical" stream or current
of (charged) particles, and compare the result we get with Ohms law. |
 |
First, lets define an electrical current in a wire in terms of the carriers flowing through
that wire. There are three crucial points to consider |
 |
1. The external electrical current as measured in an Ampèremeter is the result
of the net current flow through any cross section of an (uniform) wire. |
|
 |
In other words, the measured current is proportional to the difference
of the number of carriers of the same charge sign moving from the left to right through
a given cross sectional area minus the number of carriers moving from the right
to the left. |
|
 |
In short: the net current is the difference of two partial
currents flowing in opposite directions: |
|
|
|
|
 |
Do not take this point as something simple! We will encounter cases where we have to sum up
8 partial currents to arrive at the externally flowing current, so keep this in mind! |
 |
2. In summing up the individual current contributions, make
sure the signs are correct. The rule is simple: |
|
 |
The
electrical current is (for historical reasons) defined as flowing from + to –.
For a particle current this means: |
|
|
|
|
 |
In words: A technical current I flowing from + to – may be obtained by
negatively charged carriers flowing in the opposite
direction (from – to +), by positively charged carriers flowing
in the same direction, or from both kinds of carriers flowing at the same time in the proper directions. |
|
 |
The particle currents of differently charged particles then must be
added! Conversely, if negatively charged carriers flow in the same directions as positively
charged carriers, the value of the partial current flowing in the "wrong" direction must be subtracted to obtain
the external current. |
 |
3. The flow of particles through a reference surface as
symbolized by one of arrows above, say the arrow in the +x -direction, must be seen as an average
over the x -component of the velocity of the individual particles in the wire. |
|  |
Instead of one arrow, we must consider as many arrows as there are
particles and take their average. A more detailed picture of a wire at a
given instant thus looks like this |
| |
|
|
 |
An instant later it looks entirely different in detail, but exactly
the same on average! |
|
 |
If we want to obtain the net flow of particles through the wire (which
is obviously proportional to the net current flow), we could take the average of the
velocity components <v+x> pointing in the
+x direction (to the right) on the left hand side, and subtract from this the average <v–x> of the velocity components pointing in the –x direction (to the left)
on the right hand side. |
|
 |
We call this difference in velocities the drift
velocity
vDof the ensemble of carriers. |
|  |
If there is no driving force, e.g. an electrical field, the velocity vectors are randomly distributed and
<v+x> = <v–x>; the drift velocity and thus net current is zero as it should be. |
 |
Average properties of ensembles can be a bit tricky. Lets look at some properties by considering the analogy
to a localized swarm of summer flies "circling" around like crazy,
so that the ensemble looks like a small cloud of smoke. A more detailed treatment can be found in 1.3.5. |
|
 |
First we notice that while the individual fly moves
around quite fast, its vector velocity vi averaged over time
t, <vi>t,
must be zero as long as the swarm as an ensemble doesn't move. |
|
 |
In other words, the flies, on average, move just as often to the left
as to the right, etc. The net current produced by all flies at any given instance or by one individual
fly after sufficient time is obviously zero for any reference surface. |
 |
In real life, however, the fly swarm "cloud" often moves slowly
around - it has a finite drift velocity which must be just the difference between the
average movement in drift direction minus the average movement in the opposite direction. |
|  |
The drift velocity thus can be identified as the proper average that
gives the net current through a reference plane perpendicular to the direction of the drift velocity. |
|  |
This drift velocity is usually much smaller than the average magnitude of the velocity <v> of the individual flies. Its value is the difference of two large numbers - the average velocity
of the individual flies in the drift direction minus the average velocity of the individual flies in the direction opposite to the drift direction. |
 |
Since we are only interested in the drift velocity of the ensemble of flies (or in our case,
carriers) we may now simplify our picture as follows: |
| |
|
 |
We now equate the current density with
the particle flux density by the basic law of current flow: |
|  |
Current density j = Number N of particles carrying the
charge q flowing through the cross sectional area F (with the normal vector f
and |f| = 1) during the time interval t, or |
|
|
|
|
 |
In scalar notation, because the direction of the current flow is clear, we have |
| |
|
 |
The problem with this formula is N, the number
of carriers flowing through the cross section F every second. |
|
 |
N is not a basic property of the material; we certainly would much prefer the carrier density
n = N/V of carriers. The problem now is that we have to chose the volume V = F
· l in such a way that it contains just the right number N of carriers. |
|  |
Since the cross section F is given, this means that we have to pick the length l
in such a way, that all carriers contained in that length of material will have moved across the internal interface after
1 second. |
|
 |
This is easy! The trick is to give l just that particular length that allows every
carrier in the defined portion of the wire to reach the reference plane, i.e. |
|
|
|
|
 |
This makes sure that all carriers contained in this length, will have
reached F after the time t has passed, and thus all carriers
contained in the volume V = F· vD · t will contribute to the current density.
We can now write the current equation as follows: |
| |
| j | = |
q · N
F · t |
= | q · n · V
F · t | = |
q · n · F · l
F · t |
= | q · n · F ·
vD · t
F · t |
|
|
 |
This was shown in excessive detail because now we have the fundamental
law of electrical conductivity (in obvious vector form) |
|
|
|
 |
This is a very general equation relating a particle current
(density) via its drift velocity to an electrical current
(density) via the charge q carried by the particles. |
|
 |
Note that it does not matter at all, why
an ensemble of charged particles moves on average. You do not need an electrical field as driving force anymore. If a concentration
gradient induces a particle flow via diffusion, you have an electrical current too, if the particles are charged. |
|
 |
Note also that electrical current flow without an
electrical field as primary driving force as outlined above is not some odd special
case, but at the root of most electronic devices that are more sophisticated than a simple resistor. |
|  |
Of course, if you have different particles, with different density drift velocity and charge, you simply
sum up the individual contributions as pointed out above. |
 |
All we have to do now is to compare our equation from above to Ohms law: |
| |
|
|
 |
We then obtain |
| |
| s | = |
q · n · vD
E |
:= | constant |
|
|
 |
If
Ohms law holds, s must be a constant, and this implies by necessity
|
| |
|
|
 |
And this is a simple, but far reaching equation saying something about the driving force of electrical
currents (= electrical field strength E) and the drift velocity of the particles in the material. |
|
 |
What this means is that if vD/E = const.
holds for any (reasonable) field E, the material will show ohmic behavior.
We have a first condition for ohmic behavior expressed in terms of material properties. |
|
 |
If, however, vD/E is constant (in time) for a given
field, but with a value that depends on E, we have s = s(E);
the behavior will not be ohmic! |
 |
The requirement vD/E = const. for any
electrical field thus requires a drift velocity in field direction for the particle, which is directly proportional to E.
This leads to a simple conclusion: |
|
 |
This is actually a rather strange result! A charged particle in an electrical field experiences a constant
force, and Newtons first law tells us that this will induce a constant accelerations, i.e. its velocity should increase
all the time! Its velocity therefore would grow to infinity - if there wouldn't be some kind of friction. |
|
 |
We thus conclude that there must exist some mechanism that acts like
a frictional force on all accelerated particles, and that this frictional force in the case of ohmic behavior must be in
a form where the average drift velocity obtained is proportional to the driving force. |
 |
Since
vD/E = constant must obtain for all (ohmic) materials under investigation, we may give it a name:
|
| |
vD
E | = |
µ | = Mobility = |
Material constant |
|
|
|
 |
The mobility
µ
of the carriers has the unit
[µ] = (m/s)/(V/m) = m2/V · s. |
|  |
The mobility
µ (Deutsch: Beweglichkeit) then is a material
constant; it is determined by the "friction", i.e. the processes that determine the average velocity
for carriers in different materials subjected to the same force q · E. |
|
 |
Friction, as we (should) know, is a rather unspecified
term, but always describing energy transfer from some moving body to the environment. |
|  |
Thinking ahead a little bit, we might realize that µ is
a basic material constant even in the absence of electrical fields. Since it is tied
to the "friction" a moving carrier experiences in its environment - the material under consideration - it simply
expresses how fast carriers give up surplus energy to the lattice; and it must not matter how they got the surplus energy.
It is therefore no suprise if µ pops up in all kinds of relations, e.g. in the famous Einstein
- Smoluchowski equation linking diffusion coefficients and mobility
of particles. |
 |
We now can write down the most general form of Ohms
law applying to all materials meeting the two requirements: n = const. and µ = const.
everywhere. It is expressed completely in particle (= material) properties. |
|
|
|
|
 |
The task is now to calculate n and µ from first priciples, i.e.
from only knowing what atoms we are dealing with in what kind of structure (e.g. crystal + crystal defects) |
|
 |
This is a rather formidable task since s varies over a extremely
wide range, cf. a short table with some relevant numbers. |
 |
In order to get acquainted with the new entity "mobility", we do a little exercise: |
| |
|
 |
Since we like to give s as a positive number, we always take
only the magnitude of the charge q carried by a particle. |
|
 |
However, if we keep the sign, e.g. write s
= – e · n · µe for electrons carrying the charge q = – e;
e = elementary charge, we now have an indication if the particle current and the electrical current have the same direction (s > 0) or opposite directions s
< 0) as in the case of electrons. |
|
 |
But it is entirely a matter of taste if you like to schlepp
along the signs all the time, or if you like to fill 'em in at the end. |
 |
Everything more detailed then this is no longer universal but specific for certain materials.
The remaining task is to calculate n and µ for given materials (or groups of materials). |
|
 |
This is not too difficult for simple materials like metals, where we know that there
is one (or a few) free electrons per atom in the sample - so we know n to a sufficient approximation. Only
µ needs to be determined. |
|
 |
This is fairly easily done with classical physics; the results, however, are flawed beyond repair: They
just do not match the observations and the unavoidable conclusion is that classical physics must not be applied when looking
at the behavior of electrons in simple metal crystals or in any other structure - we will show this in the immediately following
subchapter 2.1.3. |
 |
We obviously need to resort to quantum theory and solve
the Schrödinger
equation for the problem. |
|
 |
This, surprisingly, is also fairly easy in a simple approximation. The math is not too complicated; the
really difficult part is to figure out what the (mathematical) solutions actually mean.
This will occupy us for quite some time. |
| |
|
© H. Föll (Electronic Materials - Script)