|
We will look in some detail on the system Si - silicide - metal, where
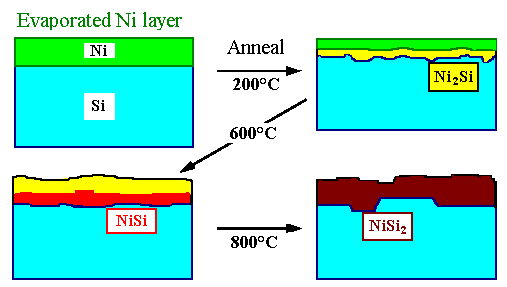
many phase boundaries can be observed. The basic experiment consists of depositing a metal (here Ni) on Si
(either in a {100} or {111} orientation), and induce some reaction by heating. |
|
 |
Three different Ni-silicides will form consecutively: |
| |
|
 |
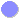
Altogether five different phase boundaries may be encountered, some of which are
shown in the picture above: |
|
 |
Si - Ni,
Si - Ni2Si and Ni2Si - Ni,
Si - NiSi and NiSi - Ni2Si,
Si - NiSi2, and NiSi2 - NiSi. |
 |
Major findings are: |
|
 |
The interface between Si and Ni does not really exist because immediately after
the (room temperature) evaporation, a thin Ni2Si-silicide layer forms between the Si and the Ni. |
|
 |
The Ni2Si layer is polycrystalline; the interface between Si and
Ni2Si seems to be incoherent - i.e. if there is any structure it is not observed with "normal"
TEM. |
 |
The interface between {111} Si
and NiSi is epitaxial, however, and thus semicoherent against all expectations: |
|
 |
NiSi is reported to crystallize in an orthorhombic
lattice; on {111} Si substrates, however, a hexagonal lattice is observed (which
can be cobtained from an orthorhombic lattice by slight adjustments of the lattice parameters). |
|
 |
The misfit is extremely large (ca. 15%) and would
require a distance of 0,6 nm for b = a/2<110> misfit dislocations. Such a small spacing
is usually considered to be too small to be meaningful - epitaxial relationships thus should not exist. The diffraction
pattern, however, indicates a clear epitaxial relationship (with a bit of polycrystallinity as indicated by the rings): |
| |
|
|
 |
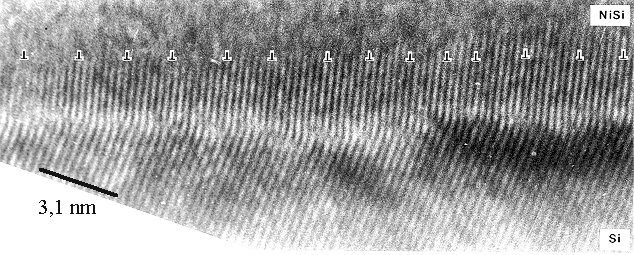
While no structure can be seen in conventional TEM, high-resolution TEM shows
pronounced misfit dislocations relieving some of the stress at a spacing of about 1,6 nm. This is one of the densest
misfit dislocation networks ever observed. The ending lattice planes are indicated by the edge dislocation symbol somewhat
above the actual interface plane. |
|
|
|
 |
The most interesting phase is NiSi2; it is the final product
after sufficient annealing at 800 °C. |
|
 |
NiSi2 crystallizes in the cubic CaF2 - structure with a lattice constant that is only 0,3% smaller than that of
Si. |
|
 |
We thus can expect an epitaxial relationship with a misfit dislocation network
at a spacing |
| |
| p | = b · |
b
(ae – am)/am
| = | b
0,003 |
|
|
|
 |
With aSi = 0,54 nm and b = a/2<110> = 0,382
nm we would expect a network with a spacing of about 130 nm. |
|
 |
What we see for an interface on a {111} plane looks like this: |
| |
|
|
 |
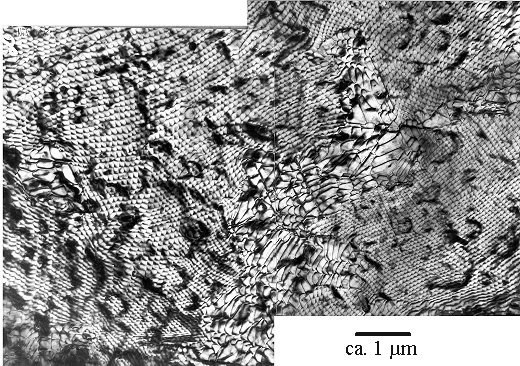
This looks rather interesting. We seem to have a simple hexagonal network of dislocations,
but we see some additional features: "Blackish" areas and an island with rather coarser structures embedded in
a sea of something with a possible hexagonal symmetry. |
 |
The reasons for these complications are two peculiarities of this interface, which
can also be found in similar systems; in particular in the Si - CoSi2 interface. |
|
 |
First, it "likes" to be on {111}-planes.
This leads to heavy facetting if the Ni layer is deposited on a Si {100} plane, but also to some facetting
on {111}. This can be seen best in cross-section; an example is
given in the illustration. We must expect that the accommodation of steps will introduce irregularities into the network. |
|
 |
Second, the interface is mostly not
in a S = 1 relation, i.e. with a direct continuation of the lattices, but in a S = 3 relation. This means that the NiSi2 is twinned
with respect to the substrate. An overview picture is shown in the link.
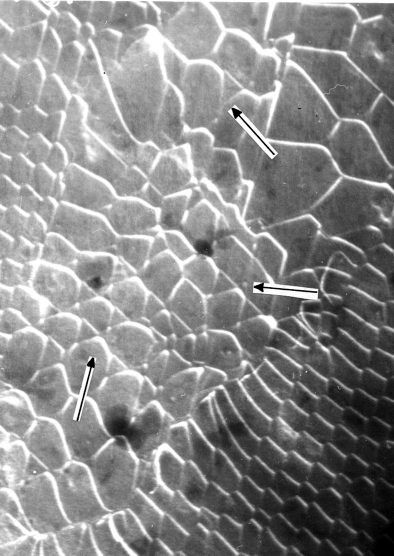
This somewhat surprising result can be obtained from a careful contrast analysis of the network with micrographs taken at
higher magnifications. The network then looks like this: |
|
|
|
|
 |
Shown is one of the "islands" in a sea of regular hexagonal dislocations. Its structure
looks somewhat familiar: The arrows point to extended stacking
fault knots as in the case of the small angle twist grain boundary on {111} in Si. |
|
 |
But in contrast to the network in the small angle twist boundary, all dislocations now are
edge dislocations; as expected for misfit dislocations. The distance is also what would
be expected for a almost fully relaxed layer of NiSi2. |
 |
The question is, of course, why this mix of S =
1 and S = 3 relations? As in the case of the low angle twist boundary encountered before, nobody knows for sure. Obviously, the energy balance
is rather similar for the two cases. |
|
 |
Very similar interfaces have been observed in the case of Si - CoSi2 interfaces,
which, except for a slightly larger misfit, have essentially the same geometry. |
 |
Despite the structural similarity to the small angle grain boundaries, the phase
boundaries add new features and open questions. To get more insights, we will now discuss the case of the interface between
(cubic) Si and (hex.) Pd2Si. |
© H. Föll (Defects - Script)