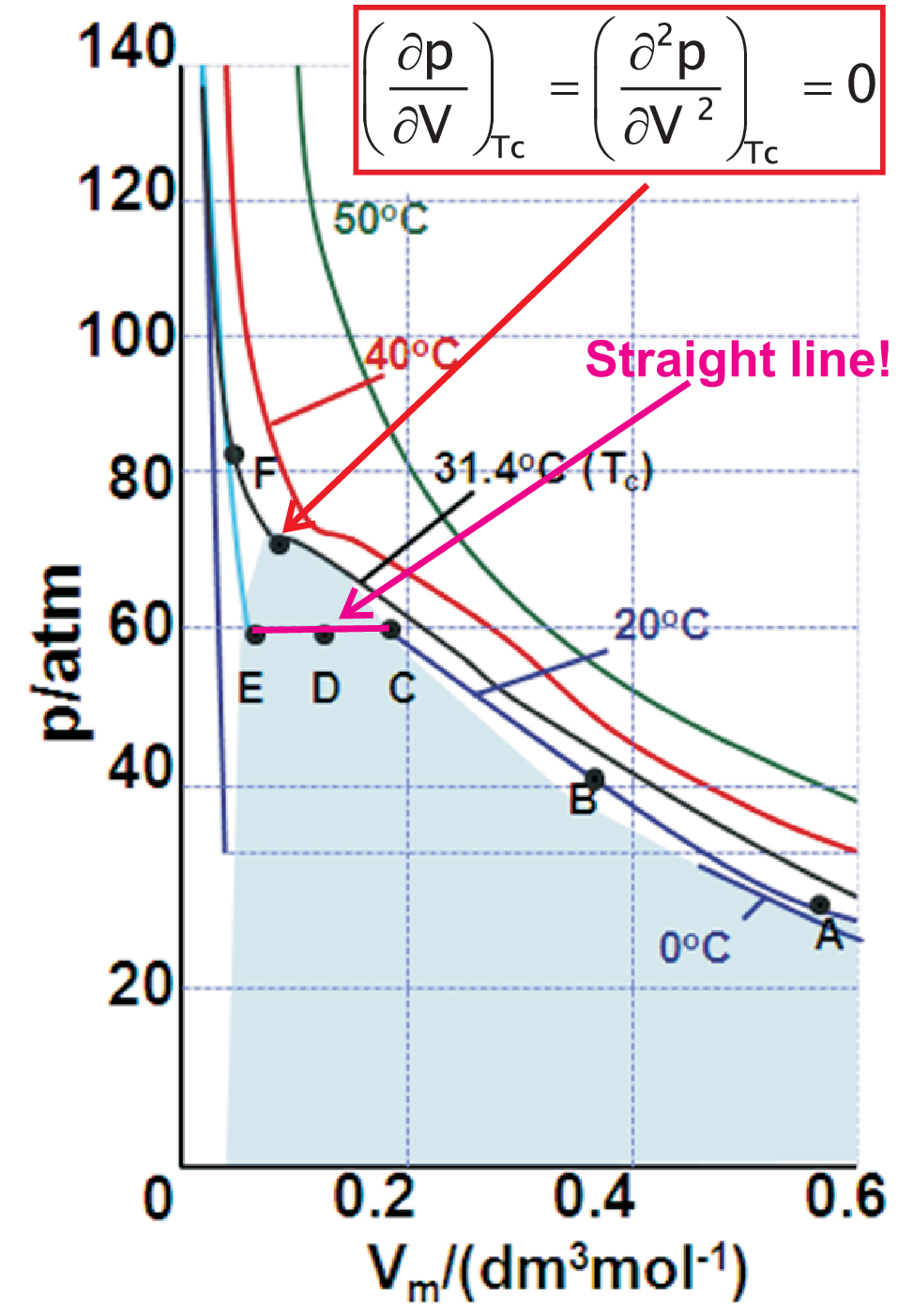
By discussing the condensation of real gases, here as an example CO\(_2\), we will learn much about the standard vocabulary of thermodynamics and various phenomena. The prefix iso (Greek: equal) is found in many phrases like isobars, isotropic, etc.. So isotherms represent data measured at constant temperature. In Fig. 1.4 several isotherms for CO\(_2\) in a \(pV\)-diagram are shown. Comparing just the shape of the isotherms a critical temperature \(T_c\) is found:
At the critical point the first and second derivative are zero. To determine the value of the critical point we need a third condition which is the thermal equation of state under consideration. In the next section we will use the Van-der-Waals approach to solve this problem.
Supercritical isotherms (\(T \gt T_c\)) show no buckles / edges. No phase separation exists but one single phase of a supercritical fluid (SCF). Under compression a SFC with high density is formed.
Subcritical isotherms (\(T \lt T_c\)) show buckles / edges. Generally such
edges indicate phase separation implying many properties we will discuss later in detail. Here phase separation means that
a liquid and a vapor phase exist simultaneously in separated regions of the system. Under compression \(V_m\)
decreases by condensation, i.e. CO\(_2\)(g) (g: gas) is transformed into CO\(_2\)(l)
(l: liquid).
In detail the characteristic points in Fig. 1.4 indicate:
At C condensation to CO\(_2\)(l) starts
Along CDE: constant \(p\) but increase of CO\(_2\)(l) amount
Strong slope EF due to compression of pure CO\(_2\)(l)
Critical point \(p_c\), \(V_c\), \(T_c\): critical constants. The practical meaning of the critical constants will be discussed later.
The properties of gases and fluids discussed here have a large impact for physical/technical processes. E.g. to liquify gases typically high pressure is used. So one could ask the question: Is it possible to produce liquid oxygen by compression at room temperature? The answer is: NO! The temperature must be below the critical temperature, otherwise a supercritical isotherm is present.
© J. Carstensen (TD Kin I)