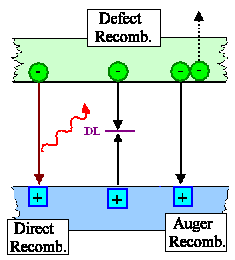
- Direct band-band recombination; producing light.
- Defect recombination; not producing light.
- Auger recombination; not producing light.
- "Exotic" mechanisms like exciton recombination; producing light in indirect semiconductors like GaP
 |
|---|
 |
|---|
 |
|---|
 |
|---|
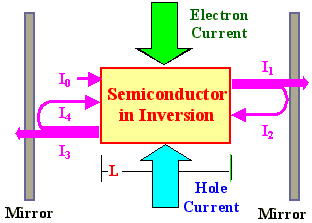 |
|---|
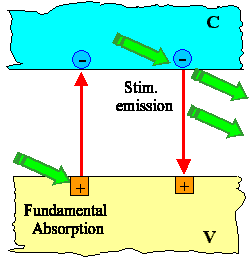
hn = hc/l = Eg
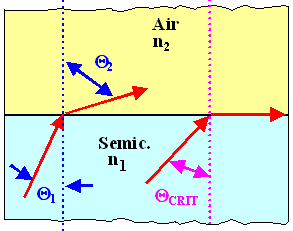
the Laser wavelength is given
| Exercise 9.2-1 | |||
| All Quick Questions to 9. |