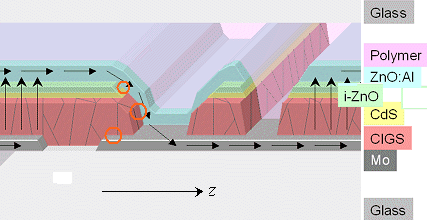
|
Thin film solar cells need to meet some key requirements: |
|
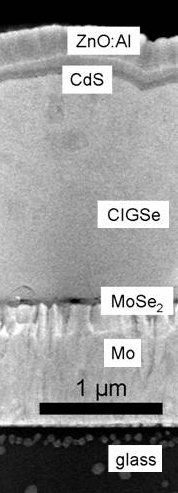 |
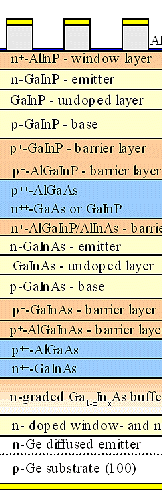 | | CIGS | Multi junction |
|
|
 |
- Process-compatible and cheap substrate Þ large area deposition.
- Suitable direct band gap Þ high absorption coefficients f
- Insensitivity to "defects"
- Technology for junction and good ohmic contacts.
|
|
 |
Major contenders in (or close) to production are: |
|
|
 |
- Amorphous Si.
- Nanocrystalline thin film Si.
- Polycrystalline thin film Si.
- The CuInxGa1-xSe2 or "CIGS" family.
- The CdTe solar cell.
- May others in R&D
| |
|
 |
The present "high potentials" are CdTe and CIGS. |
|
| |
| |
|
 |
High-efficiency multi-junction solar cells may find applications as "concentrator
cells" at the focus point of a large mirror or lens that tracks the sun. |
|
|
| |
| |
 |
CIGS and most other thin film solar cells have high internal resistances
and need to be switches in series after about 1 cm for high performance |
|
|
|
 |
This must be done automatically and in-situ as part of the production process. |
|
|
 |
A whole new technology needs to be developed for thin film solar cell mass production |
|
 |
The race between bulk Si solar cells and thin film technologies is open
in 2008; the winning technologies are to be determined. |
|
|
|
|
© H. Föll (Semiconductor Technology - Script)