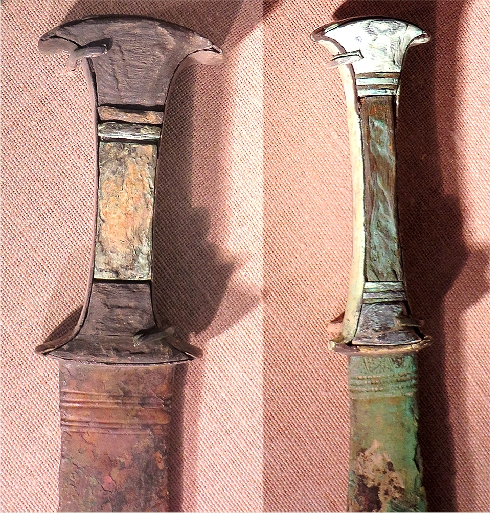Uluburun Shipwreck
 |
|
| What the divers saw Large picture | |
| Source: Photographed May 2017 in the Bodrum museum |
 |
|
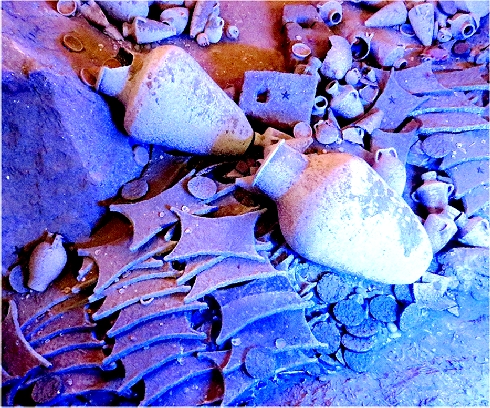
| The boat and its cargo "cut" lengthwise Large picture | |
| Source: Photographed May 2017 in the Bodrum museum |
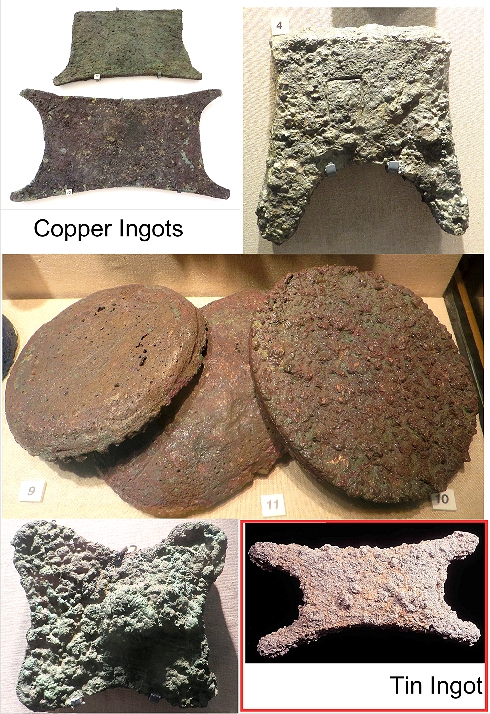
- Copper: 354 ingots of the oxhide (rectangular with handholds extending from each corner) type and 121 copper bun and oval ingots
- Tin: Approximately one ton of tin; oxhide and bun shaped ingots.
- Amphorae / Jars: At least 149 Canaanite jars (widely found in Greece, Cyprus, Syria-Palestine, and Egypt). One jar filled with glass beads, many filled with olives, but the majority contained a substance known as Pistacia (terebinth) resin, an ancient type of turpentine.
- Glass: Approximately 175 glass ingots; cobalt blue turquoise and lavender in color.
- Miscellaneous: Logs of blackwood from Africa (referred to as ebony by the Egyptians); Ivory in the form of whole and partial hippopotamus and elephant tusks; Ostrich eggshells Cypriot pottery; Cypriot oil lamps; Bronze and copper vessels. Two duck-shaped ivory cosmetics boxes. More than two dozen sea-shell rings. Beads of amber (Baltic origin); Agate, Carnelian, Quartz, Gold Faience Glass.
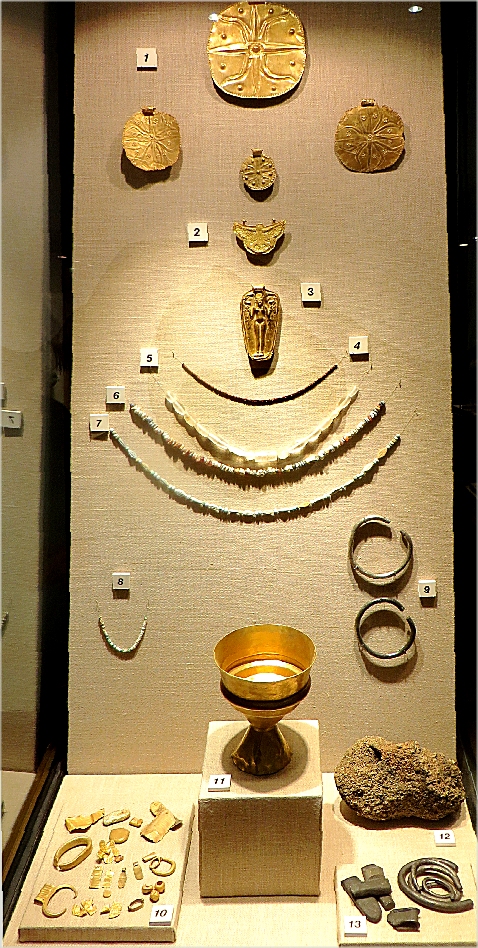
- Jewelry: Canaanite jewelry, 37 gold pieces including: pectorals, medallions, pendants, beads, a small ring ingot, and an assortment of fragments. a biconical chalice (largest gold object from wreck). Egyptian objects of gold, electrum, silver, and steatite (soap stone). A gold scarab inscribed with the name of Nefertiti. Bronze female figurine (head, neck, hands, and feet covered in sheet gold).
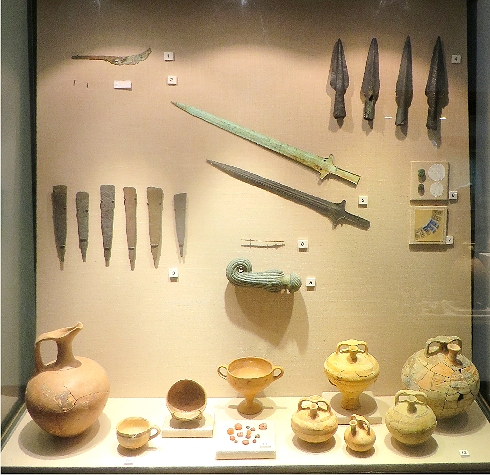
- Weapons: Arrowheads, spearheads, maces, daggers, lugged shaft-hole axe. Four bronze swords (Canaanite, Mycenaean, and Italian(?) types).
- Tools: A large number of tools included sickles, awls, drill bits, a saw, a pair of tongs, chisels, axes, a ploughshare, whetstones, and adzes
 |
|
| Some copper and one tin ingot Large picture | |
| Source: Photographed May 2017 in the Bodrum museum |